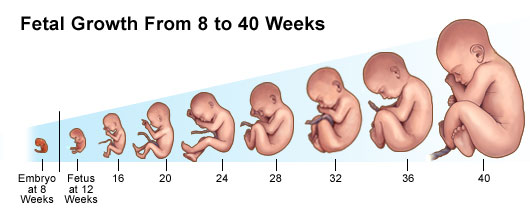
Pregnancy is a miraculous and transformative journey in a woman’s life, marked by a multitude of signs and symptoms that indicate the presence of a new life growing within. From the earliest stages to the final moments of delivery, the body undergoes remarkable changes. This comprehensive article aims to shed light on the various signs and symptoms of pregnancy, offering insights into the physical, emotional, and hormonal transformations that characterize this extraordinary experience.
Early Signs of Pregnancy:
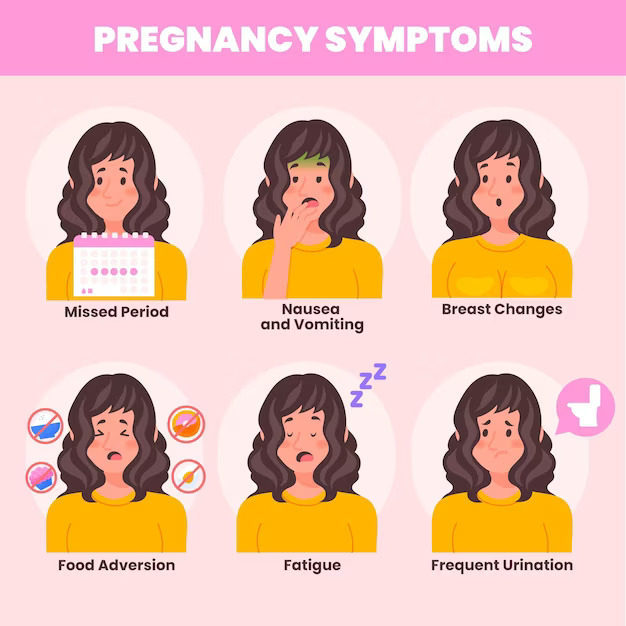
- Missed Menstrual Period:
- The most common and often the first sign of pregnancy is a missed menstrual period.
- Hormonal changes, specifically the rise in human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), contribute to the absence of menstruation.
- Morning Sickness:
- Nausea and vomiting, commonly known as morning sickness, can occur at any time of the day.
- This symptom is attributed to increased hormone levels and is experienced differently by each woman.
- Breast Changes:
- Swollen and tender breasts are a common early sign of pregnancy.
- Hormones like estrogen and progesterone lead to increased blood flow and changes in breast tissue.
- Fatigue:
- Feelings of extreme tiredness and fatigue are prevalent during early pregnancy.
- Hormonal shifts, increased metabolism, and the body’s efforts to support the developing fetus contribute to this fatigue.
- Frequent Urination:
- The growing uterus exerts pressure on the bladder, leading to increased frequency of urination.
- Hormonal changes also play a role in this symptom.
Physical Changes During Pregnancy:
- Weight Gain:
- Weight gain is a natural and necessary part of pregnancy.
- It supports the growth of the baby, amniotic fluid, and the placenta.
- Visible Changes in the Abdomen:
- As the pregnancy progresses, the abdomen expands to accommodate the growing fetus.
- Changes in the skin, such as stretch marks, may also become noticeable.
- Changes in Hair and Skin:
- Hormonal fluctuations can impact hair and skin, leading to changes such as increased hair thickness and changes in pigmentation.
- Varicose Veins and Swelling:
- Increased blood volume and pressure on blood vessels can result in varicose veins and swelling, especially in the legs.
- Heartburn and Indigestion:
- Hormonal changes relax the muscles of the digestive tract, leading to symptoms like heartburn and indigestion.
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms:
- Mood Swings:
- Hormonal fluctuations can contribute to mood swings and emotional changes.
- Expectant mothers may experience heightened emotions and increased sensitivity.
- Anxiety and Pregnancy-related Stress:
- The anticipation of parenthood and concerns about the health of the baby can lead to anxiety and stress.
- Support from partners, family, and friends is crucial during this time.
- Nesting Instinct:
- Many women experience a “nesting” instinct, an overwhelming urge to prepare for the arrival of the baby by organizing and cleaning.
Second Trimester Symptoms:
- Decrease in Morning Sickness:
- Many women experience a reduction in morning sickness during the second trimester.
- Hormonal changes and the stabilization of pregnancy contribute to this relief.
- Increased Energy Levels:
- The second trimester is often characterized by increased energy levels.
- This is a time when women may feel more comfortable and experience a renewed sense of well-being.
- Fetal Movement:
- As the baby grows, mothers can begin to feel fetal movements, commonly known as “quickening.”
- This is a reassuring sign of the baby’s health and development.
Third Trimester Symptoms:
- Back Pain and Discomfort:
- The growing uterus and the additional weight can lead to back pain and discomfort.
- Proper posture and support devices can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Braxton Hicks Contractions:
- These are intermittent contractions that prepare the uterus for labor.
- While not as intense as true labor contractions, they can be uncomfortable.
- Shortness of Breath:
- The enlarging uterus can exert pressure on the diaphragm, leading to feelings of breathlessness.
- Changes in lung capacity also contribute to this symptom.
Labor and Delivery:
- True Labor Contractions:
- Distinguishing between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labor contractions is crucial.
- True labor contractions become regular, longer, and more intense over time.
- Rupture of Membranes:
- The breaking of the amniotic sac, commonly referred to as water breaking, is a clear sign that labor is imminent.
- Cervical Dilation and Effacement:
- The cervix undergoes changes in preparation for childbirth, including dilation and effacement.
- Engagement and Descending of the Baby:
- The baby descends into the pelvis, preparing for the journey through the birth canal.
- This is a key indication that labor is progressing.
Conclusion:
Pregnancy is a transformative and awe-inspiring journey, marked by a myriad of signs and symptoms that reflect the intricate processes occurring within a woman’s body. From the early days of missed periods to the final moments of labor, the body undergoes remarkable changes in preparation for the arrival of a new life. Understanding these signs and symptoms not only empowers expectant mothers but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the incredible journey of pregnancy. As each woman’s experience is unique, this article serves as a guide to the diverse aspects of pregnancy, offering valuable insights into the physical, emotional, and transformative nature of this extraordinary phase of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Pregnancy Signs and Symptoms:
1. Q: What is the earliest sign of pregnancy?
A: The most common and often the first sign of pregnancy is a missed menstrual period. This occurs due to hormonal changes, specifically the rise in human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
2. Q: Is morning sickness always in the morning?
A: No, morning sickness can occur at any time of the day. It is a common pregnancy symptom characterized by nausea and vomiting, attributed to increased hormone levels.
3. Q: Why do breasts become tender and swollen during pregnancy?
A: Swollen and tender breasts are a common early sign of pregnancy. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone lead to increased blood flow and changes in breast tissue.
4. Q: How much weight gain is normal during pregnancy?
A: Weight gain during pregnancy is normal and necessary. The recommended amount varies, but on average, women are advised to gain between 25-35 pounds, depending on their pre-pregnancy weight.
5. Q: Why do pregnant women experience frequent urination?
A: The growing uterus exerts pressure on the bladder, leading to increased frequency of urination. Hormonal changes also play a role in this symptom.
6. Q: What are Braxton Hicks contractions, and how are they different from true labor contractions?
A: Braxton Hicks contractions are intermittent contractions that prepare the uterus for labor. They are less intense and irregular. True labor contractions become regular, longer, and more intense over time, signaling the onset of labor.
7. Q: When can I expect to feel the baby move?
A: Fetal movements, known as “quickening,” are typically felt between 18 and 25 weeks of pregnancy. However, this can vary, and first-time mothers may feel movements later.
8. Q: What causes back pain during pregnancy?
A: Back pain during pregnancy is often caused by the growing uterus and the additional weight, which can strain the back muscles. Proper posture, exercises, and support devices can help alleviate discomfort.
9. Q: What is the nesting instinct?
A: The nesting instinct is an overwhelming urge that some pregnant women experience to prepare for the baby’s arrival by organizing and cleaning the home.
10. Q: How do I know if my water has broken?
A: The rupture of membranes, commonly referred to as water breaking, is characterized by a sudden gush or a slow leak of amniotic fluid. If you suspect your water has broken, it is crucial to contact your healthcare provider promptly.
11. Q: Can stress and emotions affect pregnancy?
A: Yes, stress and emotions can impact pregnancy. High levels of stress may contribute to complications, so it’s essential to seek support and practice stress-reducing techniques during pregnancy.
12. Q: Is it normal to have mood swings during pregnancy?
A: Yes, hormonal fluctuations can contribute to mood swings and emotional changes during pregnancy. It is a common and normal part of the emotional journey of expectant mothers.
13. Q: Are there any warning signs during pregnancy that require immediate medical attention?
A: Yes, warning signs such as severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, sudden swelling of the hands and face, and vaginal bleeding should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
14. Q: Can I exercise during pregnancy?
A: Yes, in most cases, exercise is encouraged during pregnancy. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that the chosen activities are safe for both the mother and the baby.
15. Q: How do hormonal changes affect the body during pregnancy?
A: Hormonal changes, including increases in hCG, estrogen, and progesterone, play a vital role in supporting the pregnancy. These hormones contribute to various physical and emotional symptoms experienced during different stages of pregnancy.